Periodontal Probe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A periodontal probe is an instrument in 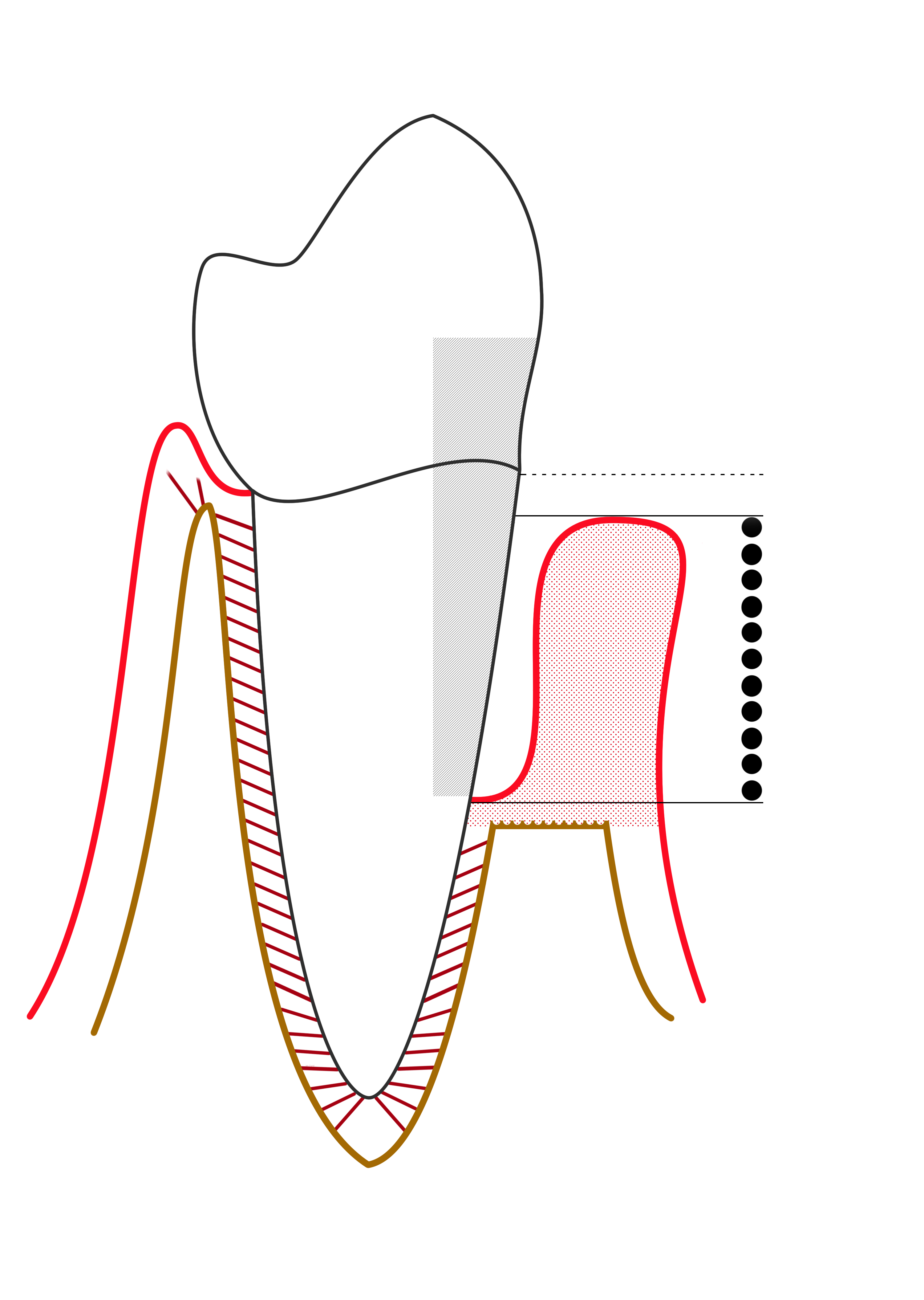
dentistry
Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions o ...
commonly used in the dental armamentarium
Dental instruments are tools that dental professionals use to provide dental treatment. They include tools to examine, manipulate, treat, restore, and remove teeth and surrounding oral structures.
Examination instruments
These tools allow dental ...
. It is usually long, thin, and blunted at the end. The primary purpose of a periodontal probe is to measure pocket depths around a tooth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
in order to establish the state of health of the periodontium
The periodontium is the specialized tissues that both surround and support the teeth, maintaining them in the maxillary and mandibular bones. The word comes from the Greek terms περί ''peri''-, meaning "around" and -''odont'', meaning "tooth". ...
. There are markings inscribed onto the head of the instrument for accuracy and readability.

Use
Proper use of the periodontal probe is necessary to maintain accuracy. The tip of the instrument is placed with light pressure of 10-20 gramsWilkins, 1999 into thegingival sulcus
The gingival sulcus is an area of potential space between a tooth and the surrounding gingival tissue and is lined by sulcular epithelium. The depth of the sulcus (Latin for ''groove'') is bounded by two entities: apically by the gingival fi ...
, which is an area of potential space between a tooth and the surrounding tissue. It is important to keep the periodontal probe parallel to the contours of the root of the tooth and to insert the probe down to the base of the pocket
A pocket is a bag- or envelope-like receptacle either fastened to or inserted in an article of clothing to hold small items. Pockets are also attached to luggage, backpacks, and similar items. In older usage, a pocket was a separate small bag o ...
. This results in obscuring a section of the periodontal probe's tip. The first marking visible above the pocket indicates the measurement of the pocket depth. It has been found that the average, healthy pocket depth is around 3 mm with no bleeding upon probing. Depths greater than 3 mm can be associated with "attachment loss" of the tooth to the surrounding alveolar bone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provid ...
, which is a characteristic found in periodontitis
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main caus ...
. Pocket depths greater than 3 mm can also be a sign of gingival hyperplasia
Gingival enlargement is an increase in the size of the gingiva (gums). It is a common feature of gingival disease. Gingival enlargement can be caused by a number of factors, including inflammatory conditions and the side effects of certain medica ...
.
The periodontal probe can also be used to measure other dental instruments, tooth preparations during restorative procedures, gingival recession, attached gingiva, and oral lesions or pathologies. Bleeding on probing (BoP), even with a gentle touch, can also occur in this situation. It is due to the periodontal probe damaging the increased blood vessels in the capillary plexus of the lamina propria
The lamina propria is a thin layer of connective tissue that forms part of the moist linings known as mucous membranes or mucosae, which line various tubes in the body, such as the respiratory tract, the gastrointestinal tract, and the urogenita ...
, which are close to the surface because of the ulceration of the junctional epithelium
The junctional epithelium (JE) is that epithelium which lies at, and in health also defines, the base of the gingival sulcus. The probing depth of the gingival sulcus is measured by a calibrated periodontal probe. In a healthy-case scenario, the p ...
(JE). The presence of bleeding is one of the first clinical signs of active periodontal disease in uncomplicated cases and should be recorded per individual tooth and tooth surface in the patient record. However, in patients who smoke, the gingival tissue rarely bleeds because of unknown factors that do not seem related to dental biofilm and calculus formation.
There are many different types of periodontal probes, and each has its own manner of indicating measurements on the tip of the instrument. For example, the Michigan O probe has markings at 3 mm, 6 mm and 8 mm and the Williams probe has circumferential lines at 1 mm, 2 mm, 3 mm, 5 mm, 7 mm, 8 mm, 9 mm, and 10 mm. The PCP12 probe with Marquis markings has alternating shades every 3 mm. Unlike the previous two mentioned, the Naber's probe is curved and is used for measuring into the furcation area between the roots of a tooth.
References
Additional references
* Summit, James B., J. William Robbins, and Richard S. Schwartz. "Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry: A Contemporary Approach." 2nd edition. Carol Stream, Illinois, Quintessence Publishing Co, Inc, 2001. . * Wilkins, Esther M. "Clinical Practice of the Dental Hygienist." 8th edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 1999. . * Hefti AF. Periodontal probing. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1997;8(3):336-56. doi: 10.1177/10454411970080030601. PMID 9260047. * Ramachandra SS, Mehta DS, Sandesh N, Baliga V, Amarnath J. Periodontal probing systems: a review of available equipment. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 2011 Mar;32(2):71-7. PMID 21473303.External links
{{Periodontology Dental equipment